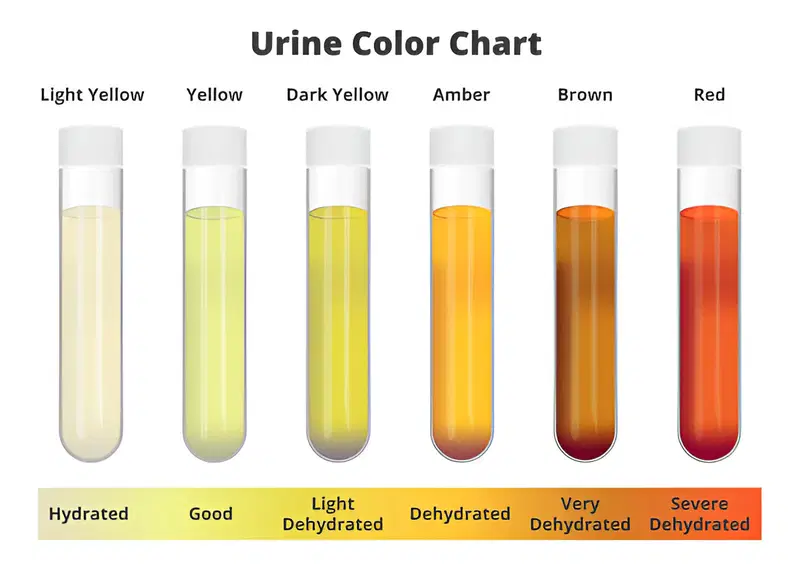
- Urine color can provide clues about hydration and potential health issues.
- Normal urine color is light yellow with a mild scent.
- Changes in color can indicate dehydration, liver or kidney issues, or other health concerns.
- Certain foods and medications can affect urine color.
- Persistent unusual colors or changes in urine smell or frequency warrant medical attention.
Understanding Urine Colors
Urine color can be an important indicator of your health. Here’s what different colors may mean:
Clear or Very Light Yellow: Well-hydrated, but beware of overhydration.
Light to Medium Yellow: Normal, healthy urine color.
Dark Yellow to Amber: Needs more water.
Orange: Dehydration, liver/bile issues, or beta-carotene intake from foods like carrots.
Pink or Red: Blood, kidney issues, or food-related from items like beets or berries.
Brown or Cola-Colored: Dehydration, liver/kidney problems, or muscle breakdown.
Blue or Green: Rare, potentially caused by medications or hypercalcemia.
Cloudy or Milky: Infection, minerals, dehydration, or excess proteins/fats.
What to Do
Monitor your urine color and smell, stay hydrated, and consult a healthcare professional if you notice unusual or persistent changes. Report any accompanying symptoms like pain or discomfort. By paying attention to urine color, you can stay informed and proactive about your health.