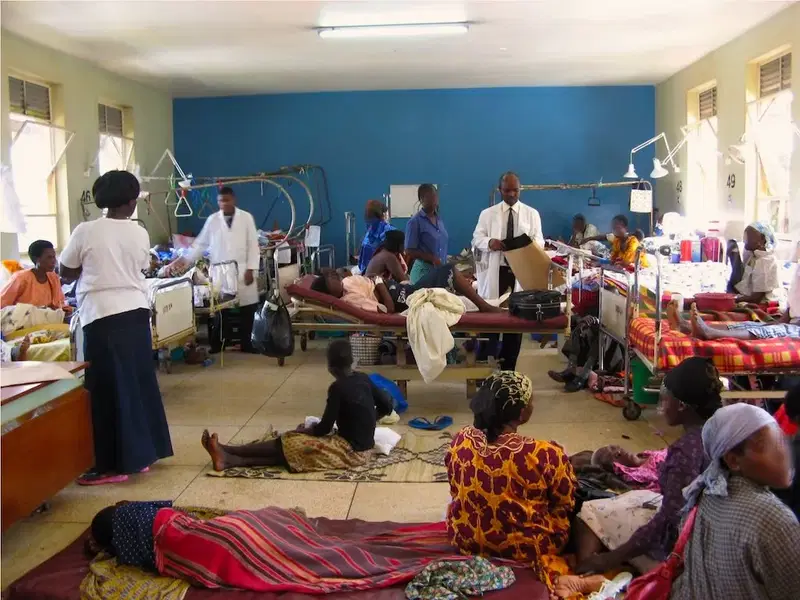
- Nigeria’s health sector faced significant challenges in 2024, despite some progress in areas like basic healthcare and disease prevention.
- Key issues included lack of funds, poor infrastructure, and insufficient healthcare workers, exacerbated by the “Japa” syndrome (exodus of healthcare experts abroad).
- The Federal Government allocated N2.5 trillion to the health sector, but this was insufficient to address the sector’s needs.
Nigeria’s health sector experienced a mixed bag of progress and challenges in 2024. While there were advancements in basic healthcare, disease prevention, and local hiring and training of doctors and nurses, the sector still faced significant obstacles.
Efforts to combat diseases like Lassa fever, malaria, and polio showed promise, thanks to improved monitoring, vaccine drives, and community participation. The country also made strides in producing its own vaccines and treatments, reducing reliance on imports. Additionally, some states saw improvements in maternal and child care, thanks to increased access to prenatal check-ups, skilled birth assistance, and post-delivery care.
However, despite these gains, the health sector continued to grapple with major challenges. The “Japa” syndrome, or exodus of healthcare experts abroad, persisted, leading to staff shortages in rural areas and compromising healthcare quality and availability. Funding for healthcare remained inadequate, limiting the government’s ability to equip facilities, purchase essential medicines, and run effective public health programs.
Poor infrastructure, including unreliable electricity supply, crumbling facilities, and limited access to clean water and sanitation, further hindered healthcare services. The threat of antimicrobial resistance was also exacerbated by inadequate infection control measures and a lack of quality antibiotics.
To address these challenges, the Federal Government allocated N2.5 trillion to the health sector, but this was insufficient to meet the sector’s needs. The government’s Renewed Hope Agenda prioritizes health, aiming to improve healthcare quality and accessibility. However, achieving these goals will require sustained efforts and investments in the health sector.